


Next: Statistical thermodynamics
Up: Chemistry in Water First
Previous: This thesis
Contents
Consider a simple reaction (R
 P) in solution and the
differential expressions for the reaction rate
P) in solution and the
differential expressions for the reaction rate
where 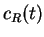 and
and 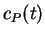 are the concentrations of the reactant R and the
product P at time
are the concentrations of the reactant R and the
product P at time 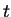 and
and 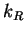 and
and 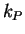 are the rate constants for the forward
and backward reactions, respectively. We assume
are the rate constants for the forward
and backward reactions, respectively. We assume 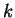 to be time independent
(cf. ref zwanzig90 for a discussion of interesting cases for which
to be time independent
(cf. ref zwanzig90 for a discussion of interesting cases for which
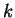 is a function of time). Furthermore, we assume that the temperature dependence
of the reaction is Arrhenius-like, which means it can be written in the form:
is a function of time). Furthermore, we assume that the temperature dependence
of the reaction is Arrhenius-like, which means it can be written in the form:
where
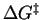 and
and
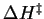 , the activation free energy and
activation enthalpy, respectively, are approximately independent
of temperature and
, the activation free energy and
activation enthalpy, respectively, are approximately independent
of temperature and 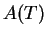 is the pre-exponential factor with only a weak temperature
dependence. The gas constant is
is the pre-exponential factor with only a weak temperature
dependence. The gas constant is 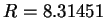 J K
J K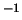 mol
mol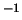 .
In the condensed phase, we can distinguish between
the relatively strong intramolecular bonds, with bonding energies which are much
higher than the energy associated with the thermal motions
(
.
In the condensed phase, we can distinguish between
the relatively strong intramolecular bonds, with bonding energies which are much
higher than the energy associated with the thermal motions
(
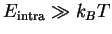 ) and the much weaker intermolecular solvent-solvent,
solute-solute, and solute-solvent interactions, with binding energies in the order
of that of the thermal motions (
) and the much weaker intermolecular solvent-solvent,
solute-solute, and solute-solvent interactions, with binding energies in the order
of that of the thermal motions (
 ). Traditionally,
the intramolecular bonds belong to the territory of the quantum chemists as the
making and breaking of these bonds (i.e. chemistry) is governed by the
electronic structure. The weak intermolecular interactions on the other hand,
are in the dominion of statistical thermodynamics as these bonds are broken
and formed continuously on the time scale of the thermal motions, so that measurements
(computations) require
averaging over the different configurations of the interacting particles.
To appreciate the title study of Chemistry in water, in which the estimation
of the rate constant
). Traditionally,
the intramolecular bonds belong to the territory of the quantum chemists as the
making and breaking of these bonds (i.e. chemistry) is governed by the
electronic structure. The weak intermolecular interactions on the other hand,
are in the dominion of statistical thermodynamics as these bonds are broken
and formed continuously on the time scale of the thermal motions, so that measurements
(computations) require
averaging over the different configurations of the interacting particles.
To appreciate the title study of Chemistry in water, in which the estimation
of the rate constant 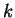 and its dependence of solvent effects belong to the important
parameters, some background information is essential on both statistical
thermodynamics and on electronic structure calculations. We will therefore start with
elementary statistical thermodynamics in this section and the section hereafter, and
then introduce the basics of the electronic structure calculations and the happy
marriage of these two fields in the method of Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics
in the sections 2.3 and 2.4.
and its dependence of solvent effects belong to the important
parameters, some background information is essential on both statistical
thermodynamics and on electronic structure calculations. We will therefore start with
elementary statistical thermodynamics in this section and the section hereafter, and
then introduce the basics of the electronic structure calculations and the happy
marriage of these two fields in the method of Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics
in the sections 2.3 and 2.4.
Subsections



Next: Statistical thermodynamics
Up: Chemistry in Water First
Previous: This thesis
Contents
Bernd Ensing
2003-06-13
![]() P) in solution and the
differential expressions for the reaction rate
P) in solution and the
differential expressions for the reaction rate