


Next: Results
Up: Method
Previous: Gas phase computations
Contents
Aqueous solution computations
We performed Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics simulations of the following
solutions: (a) HCl in water, (b) CH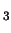 Cl in water and (c) both HCl and CH
Cl in water and (c) both HCl and CH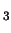 Cl in
water. For reference, a CP-PAW calculation of a pure water
sample of 32 H
Cl in
water. For reference, a CP-PAW calculation of a pure water
sample of 32 H O molecules per unit cell was also done (d). All simulations were
performed in a periodic system with the cubic unit cell containing one of each
type of solute molecules (HCl or CH
O molecules per unit cell was also done (d). All simulations were
performed in a periodic system with the cubic unit cell containing one of each
type of solute molecules (HCl or CH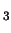 Cl or both) and 32 water molecules.
The box sizes were: 9.9684, 10.1450, 10.2463 and 9.8650 Å
for samples (a), (b), (c) and (d), respectively, yielding the experimental density of
the solution at
Cl or both) and 32 water molecules.
The box sizes were: 9.9684, 10.1450, 10.2463 and 9.8650 Å
for samples (a), (b), (c) and (d), respectively, yielding the experimental density of
the solution at 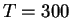 K.
The simulations of sample (c), the reactants in water, yield the central result
of the present
work. It involved the calculation of the free energy barrier for the
CH
K.
The simulations of sample (c), the reactants in water, yield the central result
of the present
work. It involved the calculation of the free energy barrier for the
CH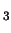 Cl + Cl
Cl + Cl reaction in water by a series of constrained CP-PAW
runs at different values of the reaction coordinate (eqn 3.2).
The starting configuration of the first run was created from a previous run of
CH
reaction in water by a series of constrained CP-PAW
runs at different values of the reaction coordinate (eqn 3.2).
The starting configuration of the first run was created from a previous run of
CH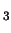 Cl in water, sample (b), at
Cl in water, sample (b), at 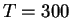 K.
A sphere-shaped cavity of radius 2 Å was created near the CH
K.
A sphere-shaped cavity of radius 2 Å was created near the CH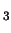 Cl molecule,
in which HCl
Cl molecule,
in which HCl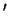 (
(
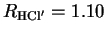 Å) was placed at a distance
from CH
Å) was placed at a distance
from CH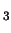 Cl equal to
Cl equal to
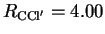 Å and with an angle
Å and with an angle
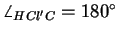 .
With the angle
.
With the angle
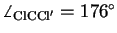 and the C-Cl distance in CH
and the C-Cl distance in CH Cl
Cl
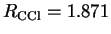 Ry
and the C-Cl distance in CH
Ry
and the C-Cl distance in CH Cl
Cl
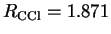 Å, this corresponds to
a value for our reaction coordinate in this initial snapshot of
Å, this corresponds to
a value for our reaction coordinate in this initial snapshot of 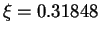 .
This value was constrained and equilibration was performed at
.
This value was constrained and equilibration was performed at 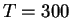 K
until there was no longer a drift in the constraint force and the potential
energy
K
until there was no longer a drift in the constraint force and the potential
energy
![$E\left[\rho\right]$](img362.png) . Then a production run
of 3-5 ps. was performed to collect statistics. After each production run,
the constraint was moved to the next reaction coordinate value
in a number of steps large enough to keep the induced
atomic velocities very small compared to their average velocities at
. Then a production run
of 3-5 ps. was performed to collect statistics. After each production run,
the constraint was moved to the next reaction coordinate value
in a number of steps large enough to keep the induced
atomic velocities very small compared to their average velocities at
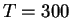 K (typically 1000-2000 steps).
This was again followed by equilibration and mean force sampling. Equilibrations
took typically 1.5-3 ps.
K (typically 1000-2000 steps).
This was again followed by equilibration and mean force sampling. Equilibrations
took typically 1.5-3 ps.



Next: Results
Up: Method
Previous: Gas phase computations
Contents
Bernd Ensing
2003-06-13